
Want to hear from us?
Sign up to receive our latest email news, offers and updates.
Pet Food Industry News
August 16, 2022The importance of minerals for pets, which minerals are essential for pet treats?
Minerals
Minerals are inorganic nutrients in the diet. When energy analysis of food is performed, all nutrients except minerals are removed, and the remaining material consists of dietary minerals, commonly referred to as "ash."
The relatively high levels of minerals in the diet are called macroelements (Table 3). Trace elements (sometimes referred to as trace elements) are required in much lower amounts but are essential for the healthy functioning of the body (Table 4)
Minerals may occur naturally in ingredients commonly used in the preparation of pet food. However, they can also be added to pet foods in the form of purified salts such as iron sulfate, zinc oxide, manganese oxide, copper sulfate, sodium selenite, calcium iodate. The bioavailability of minerals in these salts varies and must be considered when formulating mineral supplements for use in pet food.
Each mineral has several different functions, summarized below.
Calcium (Ca)
Essential for healthy bones and teeth
Background
Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the earth's crust and seawater. Calcium intake must be balanced with phosphorus (P) for healthy bone growth and maintenance.
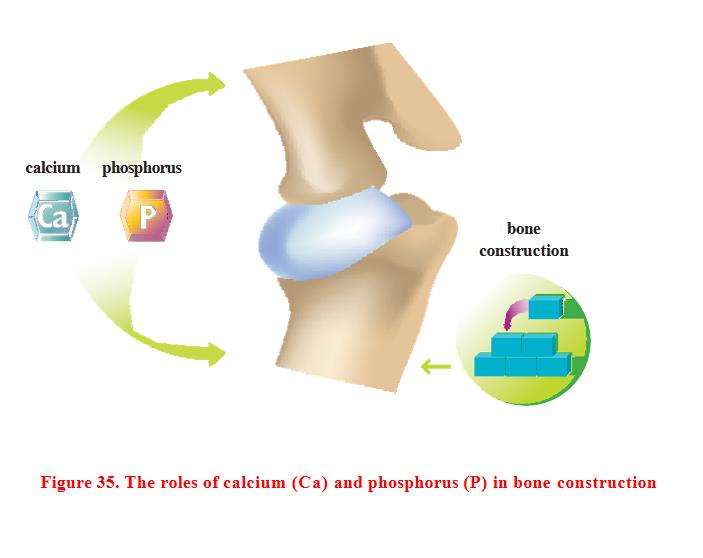
Role in the body
Calcium plays two fundamental roles in the body. More than 90% of the calcium in the body is retained in the bones and teeth, and along with phosphorus, gives these structures sufficient stiffness. Calcium also plays an important role in the transmission of information between cells and in the transmission of nerve impulses.
Common Sources
Calcium is found in the bones of mammals, birds and fish and is often added to pet food in the form of bone meal and stone meal. Dairy products also contain high amounts of calcium. Vegetables such as broccoli and cabbage are also quite good sources of calcium. Common calcium-containing mineral salts include calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, and calcium phosphate.
Deficiency and Excess
Dietary calcium levels, either below or above the required dietary level, can cause bone abnormalities. Lactation and growth require higher dietary calcium levels than other life stages. Signs of deficiency include impaired growth, while excess calcium can lead to bone abnormalities and osteomalacia.
Phosphorus (P)
Bone structure, a component of cell membranes
Background
The word phosphorus means "luminous thing". The substance was discovered in 1669 by a German alchemist who discovered that phosphorus in vapor form glowed in the dark.
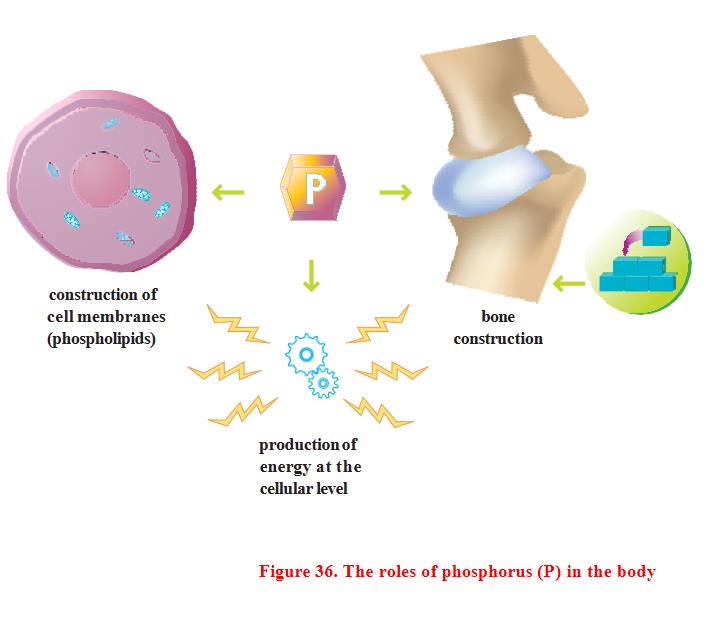
Role in the body
Phosphorus has multiple roles, each of which is equally important. Most of the phosphorus found in the body (more than 80%) is retained in the bones and teeth, where phosphorus works with calcium to make it hard. It is a component of cell membranes and is required for energy production. Phosphorus is also a structural component of the molecules DNA and RNA that carry the cell's genetic code.
Common Sources
Phosphorus is found in the bones of mammals, birds, and fish, and is often added to pet food in the form of bone meal and calcium hydrogen phosphate. Meat is also rich in phosphorus.
Deficiency and Excess
Phosphorus deficiency can lead to slow growth, loss of appetite, and bone deformities. The maximum amount of phosphorus in the diet is usually determined by calcium levels and the calcium-to-phosphorus ratio. Older cats may exhibit subclinical renal insufficiency and may be more susceptible to excess phosphorus.
Potassium (K)
Cell Function and Energy Metabolism
Background
Potassium is an alkaline mineral that oxidizes rapidly in air and is highly reactive with water. This mineral was originally isolated from potash, a type of stone, hence its name. It is the eighth most abundant mineral in the human body.
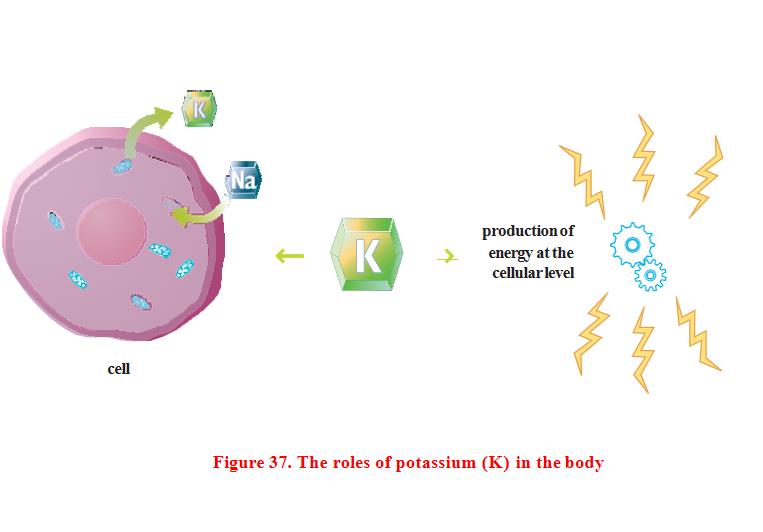
Role in the body
Potassium is the most abundant cation (positively charged ion) found in cells. Potassium is essential for the proper functioning of cells. Along with sodium, this mineral is responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance of body fluids. Potassium is also responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses and plays an important role in energy metabolism.
Common Sources
Potassium is commonly found in vegetables, meat, fish and eggs. Common mineral salts include potassium bicarbonate, potassium chloride, and potassium sulfate deficiency and excess
Although potassium deficiency is rare, agitation and muscle paralysis have been reported in potassium-deficient puppies. Diarrhea can cause a loss of potassium, which can lead to potassium deficiency if the condition persists.
The upper limit of potassium should be lower in diets designed for cats and dogs with heart disease or kidney failure. Urine acidification leads to increased potassium loss and should be supplemented with food.
Sodium (Na)
Cell balance, regulate body water balance
Background
Sodium is a soft silvery white highly reactive mineral first isolated in 1807 by Sir Humphrey Davey.
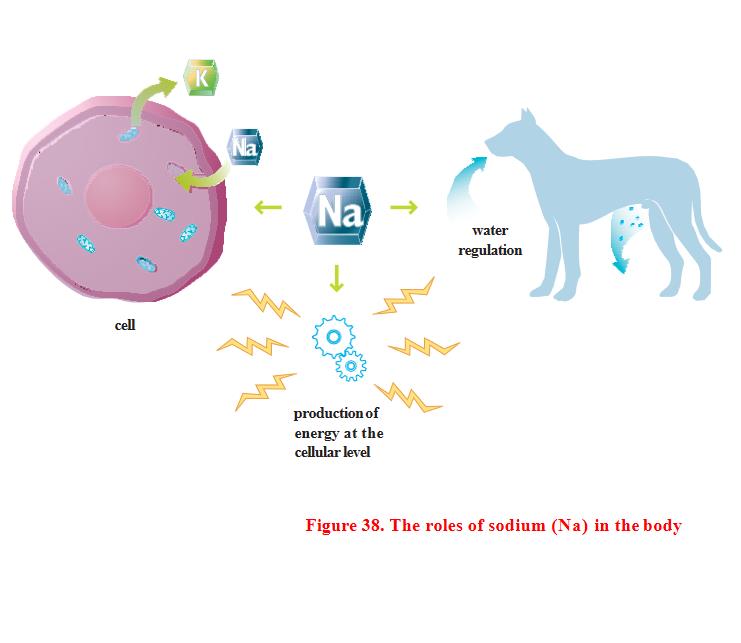
Role in the body
This mineral is essential for the healthy function of cells. It works with potassium to maintain acid-base balance and is also responsible for maintaining stress inside and outside cells. It also plays a major role in cellular energy metabolism and is involved in the generation and transmission of nerve impulses. Sodium is also important for regulating water balance, thirst, and urine concentration.
Common Sources
Sodium usually occurs naturally in the form of sodium chloride (table salt). Vegetables are generally lower in sodium, while unprocessed meats are about three times as high. Other common mineral salts include sodium phosphate and carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP).
Deficiency and Excess
Cats and dogs are rarely deficient in sodium. Deficiency symptoms include restlessness, increased heart rate, decreased water consumption, and increased urine output. High intake of sodium can cause vomiting and dry mucous membranes.
Magnesium (Mg)
Supports healthy bone structure and normal function of the nervous system
Background
Magnesium accounts for about 2% of the earth's crust and is the eighth largest element in nature. Magnesium does not exist in free form in nature because of its high activity. It is the second most abundant cation in cells and is involved in more than 300 metabolic processes.
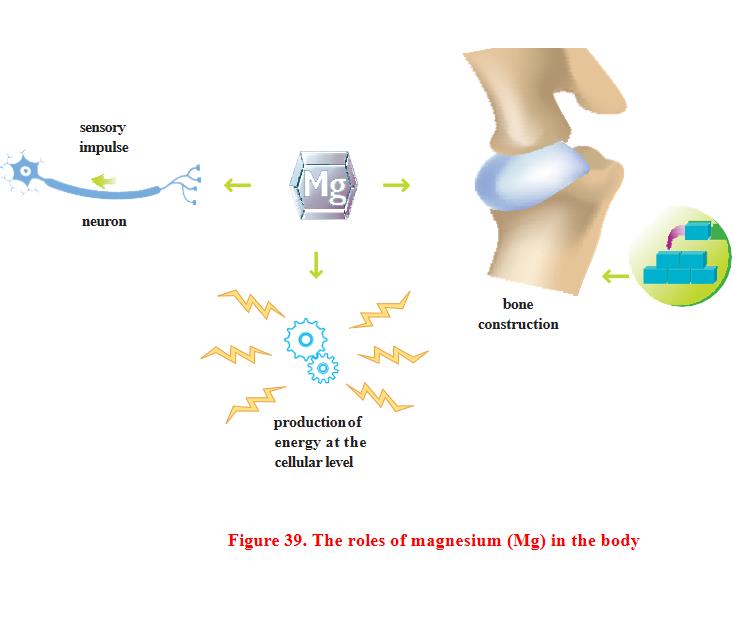
Role in the body
Magnesium plays an important role in energy metabolism, DNA and RNA metabolism, protein synthesis, muscle and nerve cell membrane function. Magnesium, along with calcium and phosphorus, is an important component of bones and teeth.
Common Sources
Magnesium is found in the bones of mammals, birds and fish and is often added to pet food as bone meal.
Deficiency and Excess
Magnesium deficiency can lead to neurological problems, including enlarged joints, paralysis, high blood pressure and loss of appetite. Excessive magnesium has been linked to cystic stone formation in cats.
Chlorine (Cl)
pH balance
Background
Chloride ion is the most common negatively charged ion in animal extracellular fluid.
Role in the body
Chloride is important for maintaining the concentration of extracellular fluid and plays an important role in acid-base balance.
Common sources
Chloride is present in limited concentrations in most foods. Therefore, the diet must be supplemented with chloride-containing salts such as sodium chloride (salt).
Deficiency and Excess
Symptoms of deficiency include weakness, poor growth, and symptoms of potassium deficiency.
Excess chloride can cause changes in calcium and potassium levels in the blood and metabolic acidosis.
Iron (Fe)
transport oxygen
Background
Iron is the most prevalent trace element in the human body, accounting for about 0.005% of the total weight
Role in the body
Iron is an important component of hemoglobin and myoglobin, the molecule that transports oxygen in red blood cells, and myoglobin does the same job in muscles. Iron also has many enzymatic functions, especially in cellular respiration.
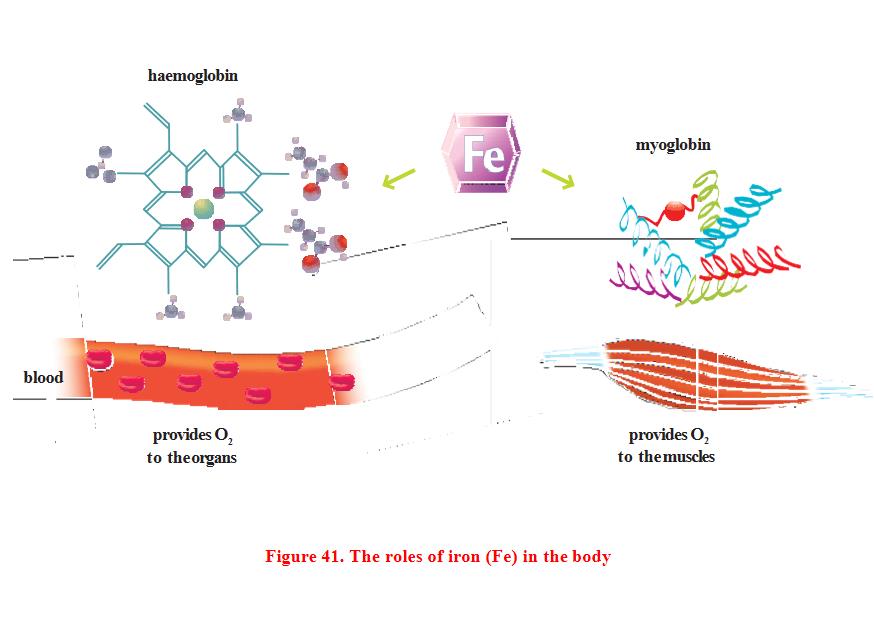
Common sources
Liver, meat, fish and green vegetables such as cauliflower and spinach are rich natural sources of iron. The utilization of iron carbonate and oxide salts is relatively poor.
Deficiency and Excess
Iron deficiency can cause poor growth, pale mucous membranes, diarrhea, and anemia. High levels of iron can lead to deficiencies in trace elements like manganese, copper, and zinc, and high levels of iron can cause vomiting and diarrhea.
If you wanna get more knowledge about dog treats, cat treats, dog dental snacks, rawhide dog treats, non-hide dog treats, rawhide free dog dental snacks, welcome to visit ctpet pet treats website: www.ctpetfood.com, www.ctpetfood.cn, www.chaotaipet.com
Welcome to contact Caroline Lee: caroline@chaotaipet.com
WhatsApp/facebook/wechat: +8615725288425

Want to hear from us?
Sign up to receive our latest email news, offers and updates.
